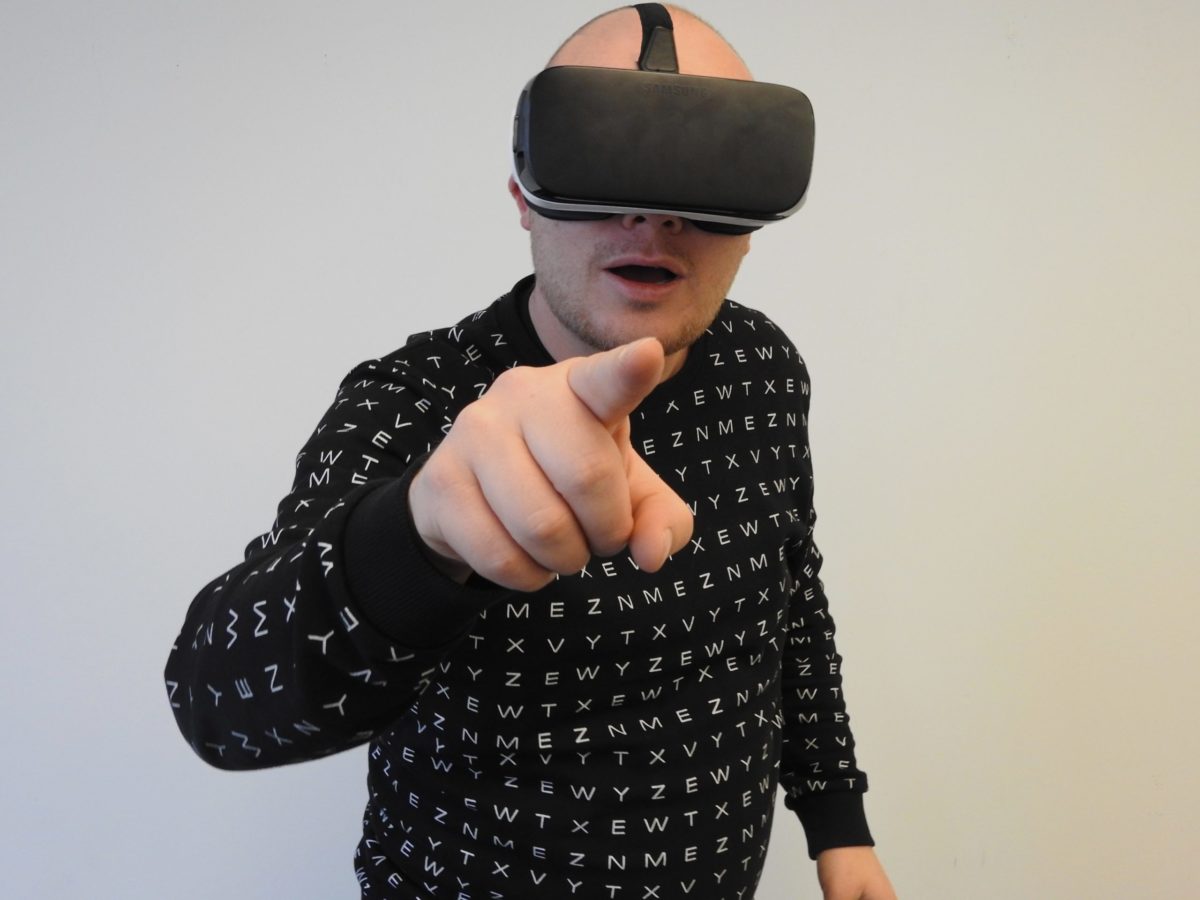
With extended reality manufacturing training, organizations can now offer new hires a simulated environment that allows them to work in a “hands-on” setting, gaining real-world, on-the-job experience — though sometimes, entirely remotely.
In an XR environment, trainees can perform necessary job duties under all the usual challenges, such as time constraints, accuracy demands, stress, weather, or distractions — but within the safety of a virtual environment.
With the Industrial Revolution of the 19th and early 20th Century, the way goods were made changed forever. Traditional methods relied on individual craftsmen to literally manufacture goods, (the root of the word being manu factum — Latin for “made by hand”). While the word, ‘manufacture’ is still used to this day, the vast majority of products are no longer hand-made.
Mass production, a growing middle class to consume more products at lower price points, (first in the West, then worldwide), and the rise of global competition has forced the manufacturing sector to continuously evolve and adapt in response. Faced with these pressures, manufacturers have sought to deploy ever-smarter machinery, like robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and numerous other automation tools to ensure consistent product quality and process efficiency — all balanced against the need to preserve worker safety.
To address these needs, once more, manufacturing has turned to technology — this time to create better, more capable, and safer workers.
As technologies have advanced, many workers have become something closer to technologists than “lever-pullers” or “button-pushers”. The increasingly sophisticated nature of machinery has led to a commensurate need for a skilled workforce capable of understanding, operating, and servicing complex processes in order to meet always-growing market demands.
Previously, manufacturers who wanted to offer such training had to go to the considerable expense, effort, and inconvenience of recreating actual work environments, or taking important tools and machinery off-line for teaching purposes.
Even the best recreations were often bottlenecked, only allowing a certain number of trainees to fully participate. Or they were limited in the number of real-life scenarios they could replicate. Or they necessitated costly cross-country or global travel from a limited number of qualified instructors. Or they resulted in sporadically uneven or non-uniform training experiences for individual team members. Or they were forced, (ironically for safety purposes) to bypass training for rare but potentially catastrophic dangers or machine faults that left trainees under-prepared in critical situations.
For manufacturing companies using a fully realized extended reality training initiative — those hurdles can be systematically overcome.
What is ‘XR’, and how does it work?
The term ‘extended reality’ (XR) actually refers to three technologies, each offering different levels of immersion, and different blends of physical and virtual interaction. At the highest level, XR includes virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR).
Augmented reality (AR) enhances real work environments by overlaying digital or virtual elements. To access common, consumer-based AR, users typically utilize a device such as a smartphone, tablet, or AR glasses. (The gaming phenomenon Pokemon GO is a classic example of mainstream use of AR technologies.)
Virtual reality (VR) allows users to fully immerse themselves in a completely simulated digital environment. A headset, (an ‘HMD’ or head-mounted display) is typically used to provide a 360-degree view of a simulated space that, in simple terms, ‘fools’ our brain into believing we are physically present in a rendered, digital world.
In mixed reality (MR), digital and physical elements co-exist and interact with one another in real-time. MR is essentially a hybrid of both augmented reality and virtual reality technologies. Requiring an MR headset, such as HoloLens by Microsoft, MR allows users to manipulate simulated forms, rooms, or models, enabling users to see things from alternate angles or perspectives or react to virtual elements in the physical world.
Because XR stimulates all our senses, we can experience simulated environments completely, with little difference compared to how we experience the real world — but with one major exception: in XR, we can execute risky activities without posing danger to ourselves or others.
What does extended reality manufacturing training offer?
XR’s immersive environments and capabilities offer significant advantages when used as a complement to traditional and computer-based manufacturing training.
By utilizing all four commonly accepted learning styles — visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic motion — XR enables trainees to build greater mental and emotional connections to their subject matter, providing them more meaningful instruction. The result: actual job experience — in a safe, simulated environment.
Distraction-Free Learning
Because participants are fully engaged with their surroundings and the information they are receiving, extended reality manufacturing training delivers an environment without distractions. The less distracted trainees are, the more they are able to focus on information they are receiving.
More Visually and Mentally Engaging Training
Because more than 90 percent of the information received by our brains is visually based, XR’s immersive, three-dimensional interactive format makes learning more visual than with traditional training. The result is trainees who retain more of what they see…and feel, with some studies showing up to 80% improvement in learning retention.
Efficient Training That Keeps Companies Working
Historically, trainers would often have to shut down production or take important machinery off-line for training purposes. XR eliminates the need for that extra cost in delivering curriculum. In addition to providing more experiential learning, XR training keeps critical manufacturing equipment functioning and contributing to overall productivity while training is being conducted.
How is XR training being used in the manufacturing sector?
XR training is finding a home in various areas within manufacturing, including:
Extended Reality Manufacturing Training Can Improve Quality Control
XR allows global organizations to ensure all trainees receive the precise training experience intended, guaranteeing critical quality control and safety measures are maintained. When all employees receive the same training, productivity levels are improved, and organizations can implement new procedures without delay using enterprise systems rollout. Employees receive the training they need no matter where they are, eliminating the need for dedicated training facilities, saving significant time and money.
Shorten Product Development Cycle
XR allows organizations to shorten the product development cycle through collaboration. Teams can access and evaluate prototypes made in other locations, catching engineering flaws or design inadequacies before moving to the production phase. XR provides global teams visual, hands-on communication from anywhere, in real-time.
Reduce Costs
Maintenance downtime can chip away at your bottom line. With better training for standard maintenance procedures comes savings in terms of the amount of time needed to safely service various machinery and equipment. XR also allows site engineers to evaluate potential systems upgrades without the need for a production shutdown. XR helps catch “bugs” and allows teams to resolve them before implementing an organization-wide rollout.
Shorten Training Time — While Increasing Productivity
Extended reality in manufacturing allows more trainees to participate at the same time compared to conventional training methods. This can be important when training seasonal or temporary workers. By reducing the amount of time you need to spend on training — some estimates suggest VR Training can speed-up training by 60% — new-hires and recruits start producing sooner, generating a faster return on your hiring and training investment.
Is your company or organization ready for XR? Reach out to PIXO today
XR allows organizations to hire employees and train them efficiently, effectively, and safely. Modern extended reality manufacturing technologies have created safer training environments, boosted employee retention and production, and increased the speed of training — while reducing its cost.
Possibly best of all, having a consistent resource of educational and training materials at your fingertips, like the PIXO Content Collection training library, for rollout at a moment’s notice, provides important “next steps” that allow companies to realize the full and complete value of an XR training program.
PIXO Has Improved VR Management to One Easy Step

Photo by Hammer & Tusk on Unsplash
